#Diagnostics & troubleshooting
Now, let's see in more detail what we consider "the right maintenance."
Always refer to your vehicle's owner's manual or consult a certified mechanic for specific repair details and safety procedures.
Bad torque converter symptoms: How to diagnose & fix
A torque converter is a crucial component in vehicles’ automatic transmission systems. It serves as a fluid coupling device that allows the engine to transfer power to the transmission and ultimately the wheels.
However, torque converters can sometimes fail due to a variety of reasons. One common issue is fluid contamination or deterioration, leading to decreased efficiency and overheating.
Recognizing early signs of a malfunctioning torque converter can prevent hefty repair costs.
What is a torque converter?
A torque converter is a key component in vehicles with automatic transmissions. It allows the transfer of power from the engine to the transmission and eventually to the wheels.
Though a torque converter may not be visible, this hidden device is crucial in delivering a smooth driving experience.
Though a torque converter may not be visible, this hidden device is crucial in delivering a smooth driving experience.
Picture the torque converter as a doughnut-shaped device that sits between the engine and the transmission. Inside, it’s filled with transmission fluid, the medium for transferring torque. This fluid-based system allows your engine to keep running while your vehicle is stopped, such as when you’re idling at a traffic light.
Essentially, it replaces the need for a clutch in automatic vehicles, allowing for the same function of disconnecting and reconnecting the engine from the transmission, but in a much more seamless and automated way.
The torque converter offers a major benefit by preventing the engine from stalling when the vehicle slows or comes to a stop. Additionally, it enables smooth gear shifts without requiring a clutch pedal, making driving easier and more comfortable for those with automatic transmissions.
Essentially, it replaces the need for a clutch in automatic vehicles, allowing for the same function of disconnecting and reconnecting the engine from the transmission, but in a much more seamless and automated way.
The torque converter offers a major benefit by preventing the engine from stalling when the vehicle slows or comes to a stop. Additionally, it enables smooth gear shifts without requiring a clutch pedal, making driving easier and more comfortable for those with automatic transmissions.
How does a torque converter work?
In vehicle torque converter acts as a hydraulic coupling connecting the engine to the transmission.
In simple terms, imagine two electric fans placed facing each other. When you switch on one fan, the air it blows causes the other fan's blades to rotate. This is a great way to visualize the basic principle behind a torque converter. However, instead of air, a torque converter uses a transmission fluid to transmit power.
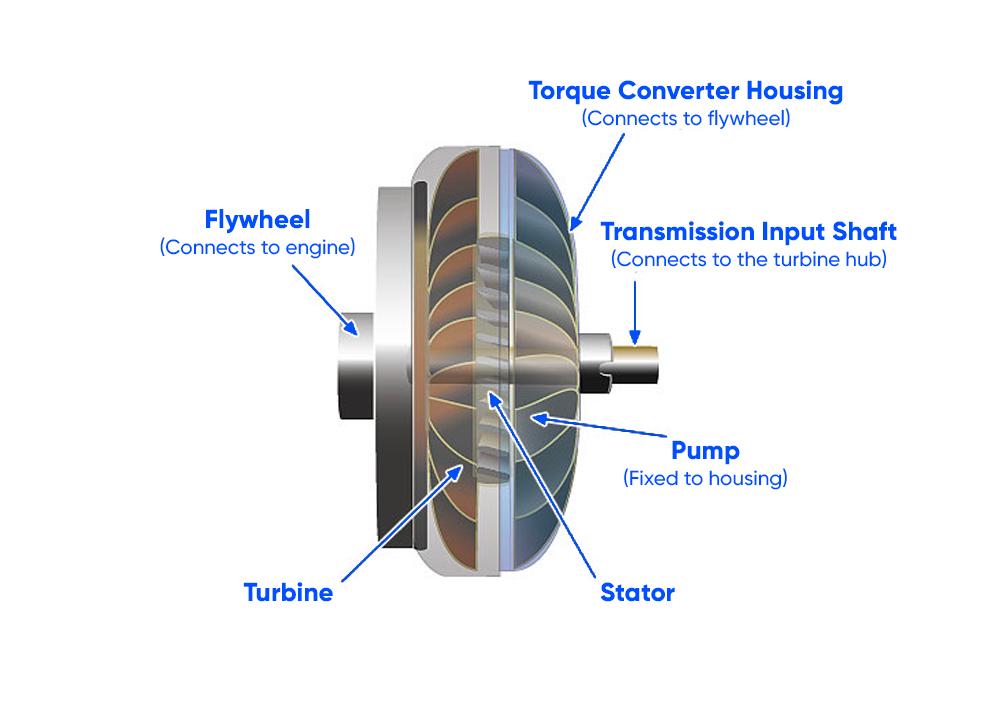
Now, let's delve deeper into the torque converter and better understand its key components:
- Flywheel (engine's flex plate). Attached to the engine, the flywheel is the driving force. It's akin to the first fan that's switched on, setting everything else into motion.
- Pump (impeller). Fixed to the torque converter housing, the pump is like our blowing fan. When the engine spins the flywheel, the pump also spins, circulating fluid throughout the converter.
- Turbine. The turbine is connected to the vehicle's transmission input shaft, acting much like the second fan that isn't powered itself but spins in response to the fluid moved by the pump. This spinning motion is transferred to the gears of the transmission.
- Stator. Located in the center, the stator redirects the transmission fluid returning from the turbine back to the pump. This redirection is crucial for increasing efficiency and torque when the vehicle is accelerating from a stop. At steady speeds, the stator's job is less critical, but it's vital for a smooth and efficient takeoff.
- Torque converter housing. This houses all the components and connects to the flywheel, ensuring that the engine's rotary motion is contained and transferred efficiently.
What does a torque converter do in automatic transmission?
When a vehicle is at a stop or idling, the impeller spins, creating fluid movement within the torque converter. As you press the accelerator pedal, the impeller spins faster. This leads to more forceful fluid flow.
This fluid flow strikes the turbine blades, which causes them to rotate and transfer rotational energy to the transmission’s input shaft.
When the vehicle accelerates, the stator rotates freely, allowing fluid to return from the turbine and flow through it without much resistance.
This fluid redirection helps increase the torque transmitted to the turbine. However, during deceleration, the stator locks, preventing the reverse fluid flow and minimizing power loss.
Overall, a torque converter allows the engine to keep running while the vehicle is stationary. It also gives smooth engagement from a standstill and provides the necessary torque multiplication for efficient acceleration.
Which vehicles have torque converters?
Typically, most automatic transmission vehicles have a torque converter. Also, while some Volkswagen Group (VAG) and BMW models employ dual-clutch systems, others, especially luxury models, utilize torque converters.
Cars with manual transmissions, electric vehicles, those with dual-clutch transmissions like the DSG (Direct Shift Gearbox) found in many VAG models, and vehicles with CVT (Continuously Variable Transmissions) and AMT (Automated Manual Transmissions) – don't use torque converters.
What are the bad torque converter symptoms?
A torque converter can malfunction for a variety of reasons, and these issues can lead to poor performance, reduced fuel efficiency, and even complete transmission failure. Some common symptoms of failing torque converter include:
Dirty transmission fluid
Transmission fluid can become contaminated with debris, dirt, and metal particles and lead to poor lubrication, overheating, and increased friction within the torque converter.
Automatic transmission fluid leaks
Leaks in the torque converter's seals, gaskets, or transmission fluid lines can lead to a drop in fluid levels, which can negatively impact performance and overheating.
Clutch slipping
Even though automatic transmissions do not have a traditional mechanical clutch plate, they still have clutch packs. If these clutches wear out, break, or fail to engage properly, it can lead to slipping, shuddering, or loss of power transfer.
Overheating
If the transmission fluid isn't cooled properly or if the vehicle is subjected to heavy loads or towing without the appropriate transmission cooler, the torque converter can overheat, leading to fluid breakdown and component damage.
Rough acceleration
When an automatic car's transmission fluid is low or dirty, it can lead to hesitant and jerky gear shifts during acceleration. Worn internal transmission parts can also cause the vehicle to struggle to pick up speed smoothly.
Gear slippage
If the transmission fluid isn't at the right level or has lost its integrity, it may result in gear slipping, which feels like the car is changing gears for no reason. Additionally, damaged internal components such as worn clutches or bands can cause the car to slip out of gear, leaving you with an uneasy and unpredictable drive.
Gear shift problems
Malfunctioning solenoids or valves can disrupt the hydraulic pressure and flow within the torque converter, resulting in erratic shifting and poor performance.
Rough idling
Among many other reasons why a car shakes when idle, contaminated transmission fluid can cause a rough idle, where the car feels bumpy and unstable while sitting still. Malfunctioning torque converter components, such as a damaged stator, can also lead to a shaky experience even when the car isn’t moving.
Important note: Symptoms of a bad torque converter can vary depending on vehicle model. Symptoms can range from transmission slipping, shuddering during acceleration, rough idling, shaking in certain gear, unusual noises, delayed or rough shifting, and even complete transmission or torque converter failure.
What does a torque converter sound like when it’s going bad?
A failing torque converter often makes unusual noises. These can include grinding, whining, or rattling noises that get louder as you accelerate.
The noise typically comes from worn or damaged internal components struggling to operate smoothly.
Can I drive with a bad torque converter?
Better not to. Driving with a bad torque converter can worsen the damage over time and potentially lead to complete transmission failure.
While you might be able to drive short distances, it’s best to have your car inspected by a mechanic as soon as possible to avoid more expensive repairs down the road.
While you might be able to drive short distances, it’s best to have your car inspected by a mechanic as soon as possible to avoid more expensive repairs down the road.
How long do torque converters last?
Torque converters are generally designed to last as long as the vehicle's lifespan or as long as the transmission – which could be around 200,000 miles. Of course, it all depends on your driving habits and maintenance.
If you take proper care, like using the right transmission fluid, avoiding overheating, and doing routine checks, you'll extend your vehicle's lifespan.
Now, let's see in more detail what we consider "the right maintenance."
How to prevent a torque converter failure?
Treating your car right can save you a lot of hassle and unplanned expenses. Here are some steps you can take to prevent torque converter problems:
- Use the right transmission fluid. Using the wrong type of fluid can lead to torque converter and transmission problems.
- Avoid overheating. Ensure your vehicle's cooling system is in good condition and avoid heavy towing or driving in extreme conditions that could cause excessive heat buildup.
- Check transmission fluid levels. Low fluid levels can lead to inadequate lubrication and low hydraulic pressure, which leads to slower engagement when shifting gears.
- Pay attention to your driving habits. Avoid abrupt starts, aggressive acceleration, and sudden stops. These behaviors can put extra stress on the torque converter and transmission.
- Use parking brake. When parking, engage the parking brake before shifting into "P." This reduces the strain on the parking pawl within the transmission, which indirectly affects the torque converter.
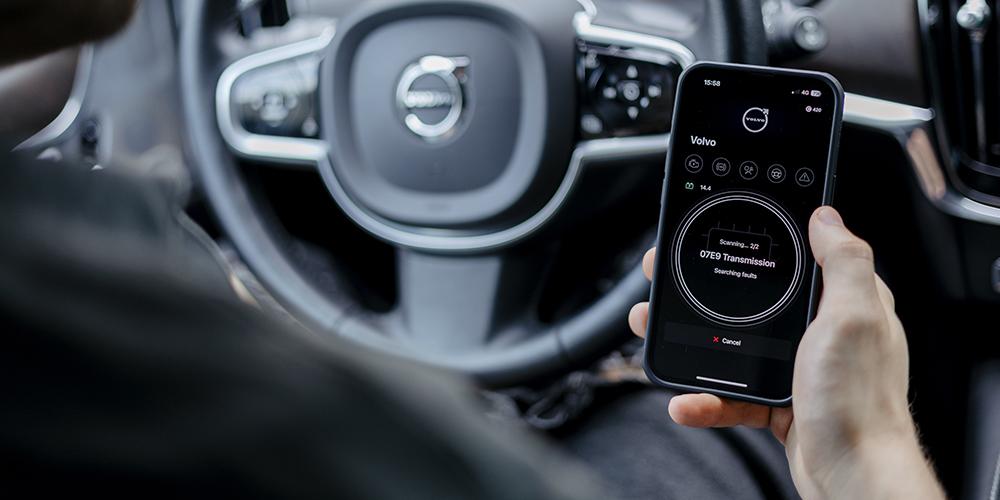
- Perform regular checks. Using scanning or diagnostics tools like OBDeleven 3 is a great way to keep track of your vehicle's performance and health. It can help you identify any issues with your transmission system by showing you the transmission fault codes.
Additionally, you can view live data parameters like torque converter hydraulic pressure, transmission fluid temperature, selected gear, and torque converter clutch slipping, which can help you stay on top of your car's maintenance needs.
To wrap up
The torque converter's health is paramount for smooth driving. Preventing its malfunction requires a combination of responsible driving practices and regular maintenance.
By being proactive and attentive, you can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your vehicle's torque converter and transmission. OBDeleven is here for you to OBDeleven is here to help you keep an eye on your vehicle's health – whenever you need, easily.
Disclaimer: Advice, how-to guides, and car care tips on our blog are intended as helpful resources for general maintenance and repairs. While we strive for accuracy, the information is provided to the best of our knowledge and should be used at your own discretion and risk.
Always refer to your vehicle's owner's manual or consult a certified mechanic for specific repair details and safety procedures.
OBDeleven 3 ULTIMATE Pack
Comprend le dispositif OBDeleven 3, le forfait ULTIMATE (12 mois), un support magnétique pour téléphone et une pochette de transport
€259.99